According to Maheshwari (2004) an organisation is defined as ‘an action, in which different person’s compromise something of importance whether merchandises and services for mutual benefit and profit’.
Next, According to Watson and Gallagher (2005) organisation strive to get outcomes by planning, developing and sustaining a system of co-ordinated undertakings in which persons and groups of people work supportively under leadership towards ordinarily agreed and established objectives.
Types of business organisation
There are different types of businesses organisations which depend upon its legal status, sector or industry, size and scope inclusively. Below, there are clarifications upon the business organisation legal structure as it is operating in the United Kingdom business environment.
- Sole trader
Sole trader designates any business organisation that is maintained and well-ordered by one individual, even though the business may employ personnel like a corner shop or local newsagent shop, hairdressers, plumbers or photographers
Sole traders do not have a distinct lawful existence from their proprietor. As a consequence, the proprietors are individually liable for the firm’s amount outstanding, duties, liabilities and may have to do repayment by his own pocket that demonstrate the unlimited liability .
Advantages of sole trader
- The organizations are generally small, and stress-free to set up.
- The organization requests small quantity of capital needed to invest, which eases the original start-up budget.
- Easier to preserve inclusive business control, since the owner has a hands-ontactic to managing the business while making any decisions without referring to anyone.
Disadvantages of sole trader
- The sole trader has nobody to portion the business responsibility. The owner has to deal with all duties such petty cash or accounting.
- Sole traders frequently work extended hours and discover it challenging to take holidays, or time off because of the commitment.
- Business development and expansion is also inadequate by regard to the amount of capital investment which is so limited.
- the risk of unlimited liability, where the sole trader can be required to trade private assets to cover any professional arrears.
- Partnership
Partnerships are businesses possessed and controlled by two or more individuals. An agreement named a deed of partnership is generally drawn up. A deed of partnership states the category of partnership, how much investment each party has funded, and how much incomes and losses will be shared. Partners have unlimited liability.
Advantages
- The sole trader is shared responsibility which allowing specialization, where one partner’s strong point can supplement another’s.
- More individuals are contributing capital, which lets for additional flexibility in running the corporate.
- Less time burden on different partners.
- business decisions based on consultation
Disadvantages
- Partnership derives from mutual obligation.
- Disputes can rise over conclusions that have to be prepared, or about the work one partner is placing into the firm associated with another.
- The sharing of profits can root difficulties. The deed of partnership arrays out who should acquire what, but can be disappointment.
- A partnership has unlimited liability.
- Private limited company
Public limited company
Limited company has distinctive status in the eyes of the law. These types of company are incorporated, which means they have their individual legal characteristics and can prosecute or possess assets in their personal right. The rights of a limited company are divided up into equivalent measures called shares.
Because limited companies have their individual legal identity, their holders are not personally legally responsible for the business’s debts. The shareholders have limited liability, which is the most important benefit of this category of business legal structure.
Advantages of public limited company
- Better access to capital, raising share capital from current and new financiers
- Liquidity, shareholders are capable to purchase and trade their shares
- Value of shares, the value of the business is publicized by the market capitalization upon the share price
- The prospect to simply make more acquisitions
- To offer a company a more prominent profile
Disadvantages of public limited company
- Once registered on a stock exchange, the business is probable to have a considerable larger quantity of external shareholders
- Financial markets will oversee the value of the business through the dealing of the business’s shares
- Better public assessment of the business’s financial performance and arrangements
ZARA Company
Zara Company is a Spanish outfit and accessories store established in Arteixo, Galicia. The company was established in 1975 by Amancio Ortega and RosalíaMera. Zara is the foremost product of the Inditex group, the world’s prevalent apparel retailer.
Define stakeholder
Friedman, A.L. and Miles, M (2006) define the stakeholders as ‘any person or group of persons whose wedged or being affected by the achievement of the organization objectives and intentions’.
Further, Gibson (2000:245) also summaries that the stakeholders are a group of people with whom the business interconnects and any person or who set of individuals who can affect or is affect by the activities, conclusions, guidelines, practices, or objectives of the organization.
Stakeholders Classifications
There are two classifications of stakeholders which comprise the internal and the external stakeholders.
Internal Stakeholders: executives, administrators, and employees. They are also called primary stakeholders because they have profitable relationship with the company.
External stakeholders: considered as secondary stakeholders in the company because they are indirectly related to the business organization. They are included the government’s organizations, the pressure groups, media and resident groups.
Enlist the stakeholder of Zara
- Customers
- Workers
- Managers
- Directors
- Bankers
- Taxation and governments agencies
- Local and general public
- Local community
- Shareholders
- Environmental groups
- Suppliers
What are the objectives (needs and expectations) of these stakeholders and what strategies are employed by the organisation to meet these objectives?
|
Stakeholders |
Need and expectations |
Strategies |
|
Customers |
Speedy reply to consumer demands Consumer care that is segmented by state (10 languages) and service which lets to deal with the clients |
– In order to reply to the need and expectations of each diverse group, Inditex remains in persistent announcement with them so that the issues those are of better interest or apprehension to them. – Zara’s vertical integration of design, Just-In-Time manufacturing arrangement, delivery and sales; flexible organizational and work structure, management of stocks on as-needed basis; quick answer policy to fashion trends and innovative information technology to maintain operations association to empower quick reply to customer’s changing difficulties (Castellano, 1993:11) – Zara guarantees that finally new clothing can be distributed, once planned and manufactured in a small cycle of four weeks. Fluctuations in standing garments are accessible at display within two weeks, more rapidly than competing companies (The Economist, 2005). |
|
Suppliers |
Pledging the Code of Conduct for Makers and Dealers is obeyed to on the supply chain |
|
|
Employees |
Devising a highly-motivated team Support employee pledge to the Code of Conduct and Accountable Performs |
|
|
Community |
Guaranteeing the programs established Having the comprehensive possible scope and control |
|
|
Environmental groups |
Application of the Environmental Policy Plan |
|
|
Shareholders |
Joining in sustainability assessments Corporate transparency |
An employee wants an increase in his salary and the Toyota will monitor the performance of the employee on annual basis and then if the employee meets the target then his salary will be increased
You need to give objectives and strategies like one given in the above example
The objectives of salary increase an important part of a compensation system with the purpose to reward workforces established on their performance accomplishments. According to ERC (2017) there are four important procedures when managing pay increases which are described below;
– Base pay grow on company performance management and objective setting methods
– Distinguish levels of pay rises
– Communicating the pay rise assessments
– providing the pay rise to employees as decided accordingly
Toyota strategy of pay increase is based on the basis pay that depends first on the class or grade of the employee within the company. Further, the wages is based on the nature of work including the following elements;
- Wages commissions
- Government arrangements
- Work experience and knowledge
- Volume of the duties
- The nature of tasks
- The level of skills involved
- Physical work
- Mental work
- Technical skills
AC1.3
Responsibilities of Toyota for the stakeholders
Provide products and services that satisfy our customers’ needs:
- Develop product quality
- Bargain better sales and services
- Reproduce customer needs in productgrowth proactively
- Encourage communication with clients
- Divulge product information decentlyand correctly
- Protect clients’ privateinformation and individual data
Shareholders to:
- Allocate revenues to shareholders
- Improve businesses proactively
- Reveal information that is wide-ranging,correct and in a timely way
- Increase ranking and assessments madeby external organizations
- Encourage stakeholder relations
For responsibilities please see the lecture notes and give some more explanation
AC2.1
Define economic system
According to Conklin (1991) economic systems states any business or corporate undertakings and measures concluded which a country builds its production and consumption conclusions.
Rosefielde (2002) mentions that economic systems are arrays of self-regulating and generally well-ordered ‘utility-seeking’ proceedings managed through deliberate transaction, common or unilateral obligation, and assignment with scarce prosperity.
Different types of economic system
- Traditional economic system
The assumption is based on tradition and chronological practice. People reflect responsibility the barter techniques or give-and-take procedures.
- Mixed market economic system
The mixed market system is the amalgamation of the elements of the free enterprise and public ownership market economic system.
- Free market economic system
Free market economy system is the structure whereby the consumers and retailers considered taking cooperative choice to generate the businesses without any intrusion, separately from the demand and supply factors or powers.
- Command economic system
The command economic system is where the administration is held responsible for development groups to produce conclusion in terms of finance, monetary, trade and industry.
AC2.2
Give economic condition of UK
The United Kingdom is functioning in free market economic system for the reason that the resources and wealth are apportioned by independent manufacturers and decision maker’s users. The United Kingdom economic comprises an assortment of private and government regulation. Consequently, the market is determined by the price of merchandises or products, and the devolution and decentralization of decision-making proceedings.
Define and explain fiscal policy and its impacts on business
According to Dwivedi (2011) fiscal policy is outlines as’ regulatory principle concerning the process of ‘public treasury’ or the administration sponsorship to bring about definite macroeconomics goals and intentions.
Fiscal policy elements
The fiscal policy elements are constituted of fiscal instrument and the target variables. Financial instrument are used by the government from its detailed predilection. Hence, the flexible incorporates tax system, financial proposal policy, government spending, transfer expenditure and public remunerations. The target variable encompasses disposable income, aggregate consumption expenditure, investments and share, imports and exportations.
Define and explain monetary policy and its impacts on Business
According to Labonte and Maknem (2006) refer to monetary policy as ‘the information, procedures, guidelines, declarations, and arrangements of the Federal Reserve that control aggregate demand or domestic disbursement.
Monetary policy components
Monetary policy features are price growths, productivity, and nominal income, and occupation, balance of payment, exchange level, domestic credit and investment market and interest level.
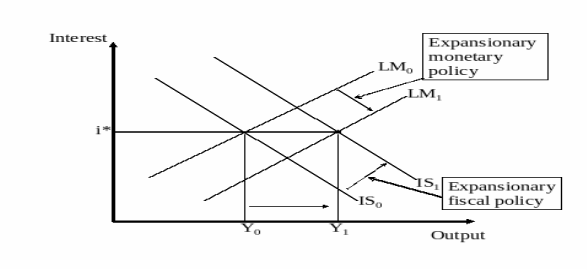
Figure: Fiscal policy and monetary policy
AC2.3
Define competition policy
The purpose of the competition policy is to decline the manipulation of monopoly supremacy which may lead to market dissatisfaction and be in contradiction of the public responsiveness and devotion.
Next, the main goals of competition policy are to promote competition; make markets work better and subsidise towards enhanced productivity in individual markets and improved competitiveness of UK businesses within the European Union (EU) single market.
Reasons for implementing competition policy
– Lower pricing opportunity for all: The simple way to improve a great market share is to deal a better price. In a competitive market, prices are depressed.
– Better quality: Competition also inspires businesses to expand the superiority of goods and services in order to attract more clients and increase market share.
– More choice: In a competitive market, businesses will attempt to sort their products different from the rest of the competition.
– Innovation: To provide this choice, and create healthier products, businesses must to be innovative and inventive
– Better rivals in total markets: Competition inside the EU supports make European companies robust outside the EU as well.
Benefits of competition policy
– Appraisal of mergers to be fewer discriminatory by legislators and self-governing bodies
– Innovative controls for supervisory body or ombudsman to scrutinize marketplaces
– Outlawing of association or cartels s, with the UK watchdogs becoming stronger
– Disqualification of directors for disagreement of the competition guidelines
– Consumer groups can complaint about uncompetitive doings
Regulation of competition policy
Regulators of competition policy are the rule-enforcers and they are chosen by the government to supervise how a market works and the consequences that result for manufacturers and customers. These regulators are the Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) and The European Union Competition Commission.
Types of regulation duties:
- De-regulation: bylaws to lessen monopoly control
- Privatization: conveying ownership
- Regulations on anti-competitive actions
- Cutbacks in import controls
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:


