Background
Brief outline of Pentland/Lacoste
Pentland was founded in 1932, as the Shoe Company, by the Rubin Family and was floated on the London Stock Exchange in 1964. The name Pentland first appeared in 1971 and was renamed ‘The Pentland Group’ in 1989. Pentland owns a number of leading sports and fashion brands including Speedo, Kickers, Ellesse, Mitre, Berghaus Kangaroo, Red or Dead, and Brasher Boot. It also has licence brands such as Lacoste Footwear, Ted Baker Footwear. Pentland headquarters is in Finchley, London, with large distribution networks in both Blackburn and Sunderland.
PENTLAND GROUP

The above is PENTLANDS mission statement. A mission statement can be describe as the goals of the organisation basically stating were they want the company to be in the future and how they aim to get there !
GOALS
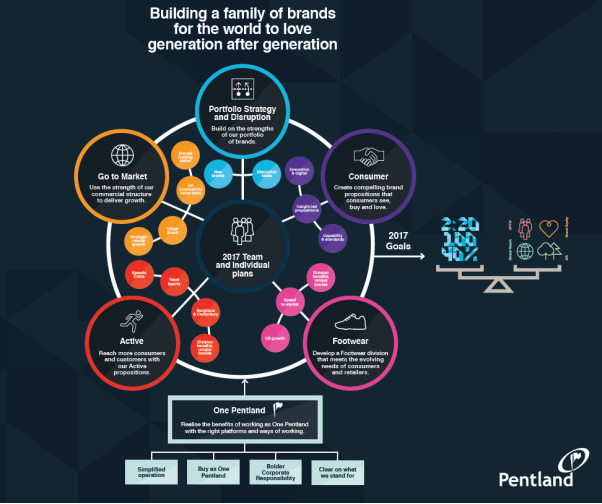
The scales represent the Pentland group goals:
Left hand side: financials sales targets global reach
Right hand side : Global reach, GPTW, Corporate responsibility, Brand equity the goal is to get these 2 sides to balance evenly.
Target of 80% of all Pentland employees saying Pentland is a great place to work (Measured by the Great Place to Work Survey ) Pentland UK to be recognised as one of the top 25 organisations
Objectives
What success looks like
One Pentland: To realise the benefits of working as One Pentland by delivering the platform and ways of working. Now split into divisions instead of brands here are 2 examples
ACTIVE: To reach more consumers and customers with our
Active propositions.
We’ve started to realise the benefits of working as a division while
Championing the unique brand offer.
Our team sports brands have grown in training, institution and
Education channels.
We’ve landed the new Berghaus proposition and Canterbury
Fitness in more distribution channels.
We’ve grown market share on t-mall and initiated our offline
strategy for Speedo China.
FOOTWEAR: To develop a Footwear Division that meets the
evolving needs of the consumer and retailer.
We’ve started to realise the benefits of working as a division while
championing the unique brand offer.
We’ve worked cross-functionally to increase our speed to market
and meet our consumer needs.
We’ve grown our footwear brands in the USA through locally relevant propositions.

UNIT 7 GOALS AND OBJECTIVES
The goal is broken down into objectives that are measurable and specific
GOAL: To be best in class for efficiency, cost, and customer focus, thereby adding value to Pentland Brands – linking into 2017 Strategic Vision
OBJECTIVES
One to one interviews:
These are conducted four times a year to discuss any concerns the employee may have. Discussing changes within the organisation and encouraging the employee to get involve in their individual objectives set out in their Personal Development Review.
Social committee :
- Make the work place more fun
- Give back days for charity work in the local community
- Organising nights out and team bonding events
- Fund raising events with the DC.
Long Service Awards
Years’ Service
5 years, 10 Years, 15 years and every five years after that
Celebrated by a bonus payment
THE MIDDLE MANGERS ROLE
- Staff Planning
- Performance Management
- Health and Safety
- Development
- Support & Motivation of Staff
- Objective setting
STAFF PLANNING: To plan staff in the DC according to budget, peak times and sickness and holiday cover.
PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT: This is an ongoing process involving communication between manager and individual (MUST BE SMART) Objectives should be set and agreed to meet organisational goals and targets etc and be reviewed in the individual’s development plan.
Important points
- Do they understand the goals
- Do they have the skills to achieve the goals
- Standards agreed and set to meet SOP
HEALTH AND SAFETY: To follow the health and safety law and the policy set by the health and safety officer
Key points
Fire drill procedure
- PPE
- MANUAL HANDLING
DEVELOPMENT: The most basic reason for development is to ensure that an organisation’s employees are able to carry out their current role. Some training may be mandatory in relation to health and safety or occupation-specific issues but much of it will be discretionary where organisations appreciate the added value that they will gain from having highly skilled and knowledgeable employees.
ONES TO ONES
- PDR FEEDBACK
- DEVELOPMENT PLAN
- PDRS
- WLM REPORTS
Support and motivation of staff
A manager should try and be positive with their attitude. Regular training should be managed within the team and all changes are communicated and updated. This can show the manager is concerned with how they do their job.
Some individuals like to receive praise for achieving their goals, this is important as it makes them feel valued. If it is a team goal sometimes when the goal is achieved they become more motivated and productive so it is important that this is shared with the team. Doing this can create good morale with the DC.
OBJECTIVE SETTING.
When setting objectives these need to be agreed and to be smart. The objectives change on a daily basis depending on work load and peak times ETC. For example when setting objectives on the packing floor, firstly we need to make sure the packer fully understands how the respective orders need to be packed and understand the SOP. The work is then planned according to a bench depending on volume and carrier. We then need to keep the packing at a minimum 85% of the agreed standard.
Evaluation process
Health and safety: To evaluate this I would use a checklist to sign that they have been shown and performed the health and safety needed, then use a show and tell to show that they have understood what they have been shown.
Some important points
- Are there rules for housekeeping and general
- Maintenance?
- Is personal protective equipment provided and
- Used?
- Are the means of investigating accidents specified
I would recommend a buddy system is used in this process and that the health and safety officer is present at the time of demonstration (MANUAL HANDLING, FLT TRAINING)
DEVELOPMENT: There are a number of reasons why the organisation should evaluate their learning and development activities and this includes the following:
- To help make decisions about what interventions should (or should not) be replicated in the future
- To provide evidence of investment in their [organisations] human capital
- To demonstrate the value that interventions bring to the organisation
Using the WLM reports and keeping the skills matrix up to date is a good way of evaluating staff development. Also an on the job demonstration is a good way to show you can perform the task safely and correctly.
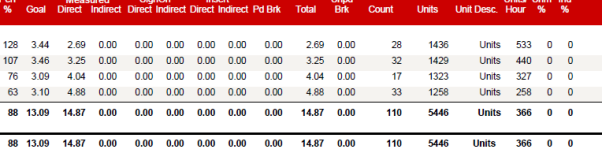
I would recommend that the WLM reports are run through with staff to show them what information or data we are using to assess their development or highlight any improvements or concerns.
Support and motivation of staff: To evaluate this I would use questionnaire and one 2 one meetings to highlight the concerns or good feedback I receive. I will then produce an action plan and keep a record of any information given or data I receive to address any situation.
In my conclusion to this I believe that the cross training to keep staff more motivated could be improved to make staff more understanding of other departments.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:


