Thinking Creatively, Thinking Critically (Group 3)
Abstracts
These days, people often use the phase of “Think out of the box”. Hence it related to term “creative thinking” and “critical thinking”. So, what are those term means? Why it is important to have these thinking skills? How does those kind of thinking fit in modern education benefit and does it benefit students especially? This paper will introduce to the creative and critical thinking not as definite, but to give an idea on what is it about. Next, apply it in Hong Kong context.
1.0 Introduction
It’s not easy to give an exact definition of creativity and critical thinking. Both aspects have varying of elements which have effects on the flow of the thinking. For creative thinking, lots of researchers came out with their own definition based on their findings. Gardner (1993) defines creativity as ‘the ability to solve problems and fashion new products and to raise new questions’. However, this definition does not cover the whole term of “creative”; creative is much more than that, but yes, it is a gist for others to branch out more on the term. Thus Gruber & Wallace (1999) say that a creative idea ‘must be new and must be given value by some external criteria’ followed by Robinson (2001) describes creativity as ‘imaginative processes with outcomes that are original and of value’.
Get Help With Your Essay
If you need assistance with writing your essay, our professional essay writing service is here to help!
Once the creative thinking has taken place, hence it leads to the next part which is critical thinking. When someone has use their creative thinking, critical thinking comes in and evaluates ideas to narrow down the focus made by creative thinking and pick idea where it is the most relevant and or have potential to succeed (Ruggiero, 1999). Encouraging students to think critically involves, among other things, helping them to distinguish opinions from facts, to evaluate evidence, and to avoid shallow and illogical thinking. This approach is very important in helping to avoid (by recognizing) manipulation, which in turn can allow intellectual independence and creativity to flourish (Browne & Keely, 1993; Mayfield, 1997; Paul, 1995). According to Meyers (1986), he gives out four elements which are needed in learning environments to encourage the development of critical thinking. First and foremost, the stimulation of students’ interest. It is required for the students to taken like in a certain topic for them to study deeper in it. Student’s with interest is much better in developing their critical thinking. Secondly, the creation of meaningful discussion. Based on their liking, the students are more comfortable and confidence to talk about it. Thirdly, the exposure to the thoughts and views of others. In this session, the students will hear various opinions and feedback from others. They will learn how to react and give comments to those who agree or disagree with their opinion. Lastly, the fostering of a supportive and trusting atmosphere. These kind of discussion is giving out positive vibes in student for their development in critical thinking. They can gain more confidence and hence helps their mind to become more mature and open to other perspective and out of their comfort zone.
2.0 Combination of Critical and Creative Thinking
The combination between two types of thinking namely critical and creative thinking had been research by many researchers in the world. According to Julie (2008), he stated that in education in order for the student to adapt with a changing world , he or she must change way of thinking different from the past. The benefits of this combination has been point out by many research such as can boots up student to take time to generate many ideas and argument , to ask penetrating questions and recognize the validity of arguments (Julie ,2008).

 2.1Difference between Critical and Creative Thinking
2.1Difference between Critical and Creative Thinking
According to Fisher ( 2002 ) , he has listed possible term to differentiate critical and creative thinking based on figure 1. According to this figure, the tendency for the people to think critical is more on left brain and think creative on right brain. Kendra (n.s) stated that the right brain has more abilities in expressive and creative task while in the left brain is more to asking that involve logic, language and analytical thinking. But , according to Julie ( 2008 ) , in order to encourage the student to think creative and critical , an approach that can combine critical and creative thinking needed to implemented instead just focussing only the distinction.
2.2 Critical and Creative Thinking in Problem Solving
 Julie (2008) stated that the benefits of critical thinking is it can help student to figure out and evaluate information that can be found via internet and mass media due to function of left hemisphere of the brain that has logical and analytic qualities ( Adam . ns). In addition to, creative thinking also has benefits in which this type of thinking can improve student’s academic performance if the student can identified their creative abilities. In order to combine both creative and critical thinking, one of the approaches that can help student is using problem solving technique.
Julie (2008) stated that the benefits of critical thinking is it can help student to figure out and evaluate information that can be found via internet and mass media due to function of left hemisphere of the brain that has logical and analytic qualities ( Adam . ns). In addition to, creative thinking also has benefits in which this type of thinking can improve student’s academic performance if the student can identified their creative abilities. In order to combine both creative and critical thinking, one of the approaches that can help student is using problem solving technique.

Problem solving technique can be defined as a process in which we perceive and resolve a gap between a present situation and a desired goal, with the path to the goal blocked by known or unknown obstacles (William, n.s).According to King (2014) , to conduct problem solving technique , there are seven step that need to focus such as analyse the problem , imagine the solution , plan solution , apply the solution , evaluate the solution , improve the solution and implement the solution.
2.3 Critical and Creative Thinking in Level of Learning


Bloom’s Taxonomy had been develop by Benjamin Bloom in order to increase higher forms of thinking in education, such as analysing and evaluating concepts, processes, procedures, and principles, rather than just remembering facts (rote learning). According to Julie (2008), bloom taxonomy consist of three domain namely affective (feeling, preferences and values) , psychomotor (physical and perceptual activities and skills) and cognitive (thinking , evaluating and synthesizing information).
Julie (2008) stated that, bloom taxonomy (figure 3) consist of six categories or level which represented in a triangle. The first level which the largest section at the base in the triangle is called Knowledge. According to bloom, in education level 95 % of test question only test the student to think at this basic level. For example in the classroom setting, the question is more likely to ask “what is the definition of ..? ”. According to Leslie, the verb that related to this level are define recall, memorize and know identify. The second level is known as comprehension which involve interpretation and classification of ideas. In this level, it more focusing on ability to create or interpret meaning from material such as report recognize, describe discuss and differentiate. For example question that related such as ‘which is the best answer..?’ and more like question in multiple choice exam. The third level is application which also can be defined as using learned material in new situation. In this level, it more focusing to use learned material in new and specific solution.. In the classroom setting, the student will be test on question such as “how would you show your understanding of ..?”.
The fourth level is analysis. Analysis can be defined as ability to differentiate material into component parts and present the relationship between those part. For example, the question that related to this level such as “what inferences that can you make from”. Synthesis which places in level five can explain by construct the ability to put ideas together to form new ways that unique, innovate and creative. The question such as “Can you predict the outcome if ..?” can be used in synthesis level. The last level is Evaluation in which the level more focusing on ability to conduct judgement and critique the worth of ideas based on reviewing and evidence. For example in the classroom , the question such as “ Do you agree with the action / outcomes ” can be used to understanding of evaluation level.
3.0 Malaysia Education System
Generally, Malaysia education system is divided into two; pre-tertiary and tertiary education. Pre-tertiary that includes primary and secondary education is regulated under Ministry of Education (MOE) whereas tertiary education is under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE).

Figure 4
According to Figure 4, primary education begins at age of seven and lasts for six years, referred to Year 1 up until Year 6. Students are promoted to the next year regardless of their academic performances. Furthermore, most students who had completed their primary education are admitted to go to secondary education. As secondary education lasts for five years, referred to as Form 1 to 5. As stated at Figure 4, secondary education are divided into two levels which is from Form 1 to Form 3, are known as Lower Secondary whereas Form 4 and Form 5 are known as Upper Secondary.
The government have provides 11 years of primary and secondary education to students. After successful completion of 11 years of study, students are given the option to continue their studies in post-secondary schools to get a pre-university qualification (such as Matriculation programme) or further their study at higher level institution.
3.1 Gifted Education in Hong Kong

Figure 5
The three-tier of gifted education framework was adopted in 2000. Based on this figure, the Education Bureau of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (HKSAR) stated in Education Commission Report No.4 that Hong Kong should develop a school-based programme in mainstream schools. Hong Kong Academy of Gifted Education (HKAGE) has come up with these policy where they want to develop the potential of gifted students by providing them with opportunities to receive education at appropriate levels.
According to Figure 5, here are the explanations;
- Level 1: A:To immerse the core elements advocated in gifted education i.e. High-order thinking skills, creativity and personal-social competence in the curriculum for ALL students; B:To differentiate teaching through appropriate grouping of students to meet the different needs of the groups with enrichment and extension of curriculum across ALL subjects in regular classrooms.
- Level 2: C:To conduct pull-out programmes of generic nature outside the regular classroom to allow systematic training for a homogeneous group of students (e.g. Creativity training, leadership training, etc.); D:To conduct pull-out programme in specific areas (e.g. Maths, Arts, etc.) outside the regular classroom to allow systematic training for students with outstanding performance in specific domains.
- Level 3: E:The HKAGE collaborates with tertiary institutions and other educational organizations / bodies to provide a wide and increasing range of programmes for exceptionally gifted students
To cater the educational needs of gifted students, they advocate the following guiding principles:
- Nurturing multiple intelligences is a requirement of basic education for all students and should be part of the mission for all schools
- The needs of gifted children are best met within their own schools though it is recognized that opportunities to learn with similarly gifted students are important. Schools have an obligation to provide stimulating and challenging learning opportunities for their students
- The identification of gifted students should recognize the breadth of multiple intelligences
- Schools should ensure that the social and emotional, as well as the intellectual, needs of gifted children are recognized and met.
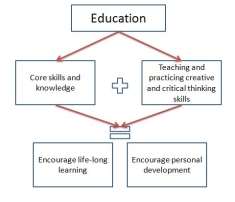 4.0 Conclusion
4.0 Conclusion
The students must be given the motivation to think, the time to develop ideas, and the collaboration and support to encourage creative and critical thinking. Connecting ideas, seeing the similarities and differences, and the most important, be flexible and curious in thinking are the important aspects that education needs in teachers and students.
References
1. Huitt, W. (1992). Problem solving and decision making: Consideration of individual differences using the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator. Journal of Psychological Type, 24,33-44.Retrievedfrom http://www.edpsycinteractive.org/papers/prbsmbti.html
2. Sicinski, A. Visual Thinking Magic The Evolution of Extraordinary Intelligence :Creativity: Merging the Left & Right Brain http://www.visualthinkingmagic.com/creativity-left-right-brain
3. King. Thoughtful Learning Blog :Teaching Innovation and Problem Solving http://thoughtfullearning.com/blogpost/teaching-innovation-and-problem-solving (Accessed 2014-04-22 )
4. Forrrester , J.C. 2008. ThinkingCreatively;Thinking Critically. Asian Social Science
5. https://www.justlanded.com/english/Malaysia/Malaysia-Guide/Education/Introduction
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:


