Trial data collection
Introduction
This research will examine the link between ethnicity and GCSE academic achievement among young people aged between 18 and 20 years old. This research will be conducted using paper questionnaires in which to gather primary data. The purpose of using a questionnaire is to gather quantitative data for analysis. The report will consist of outlining the benefits of mixed methods and quota sampling. Furthermore, interpreting what was needed to carry out the research (ethical approval), what features were included in the questionnaire and the process of the questionnaire being carried out. Finally it will discuss the results of the questionnaire and a reflection which is based on Gibbs’ reflective model.
Selection and justification of the methodology and methods
According to Gillham (2007) questionnaires have several benefits when conducting primary research, which are; respondents anonymity, lack of interviewers bias, less pressure for an immediate response, respondents can complete the questionnaire when it suits them, easy to get information from a lot of people very quickly, low cost in time/ money and finally able to gain an insight what people think and feel about the world (Bell,2005). Gillham (2007) argues questionnaires typically have a low response rate, however if the researcher is able to get a 50% of the questionnaires returned, then it can be deemed as a good outcome. The ethnicity and achievement questionnaire conducted was able to generate a response rate of 60%. From the advice of Gillham(2007)this can illustrate that the questionnaire was successful.
Get Help With Your Essay
If you need assistance with writing your essay, our professional essay writing service is here to help!
The methodology for the evaluation utilised a mixed method approach. This consists of collating both quantitative and qualitative methods to obtain the results(Bryman,2008). Quantitative research is collated in a numerical format, enabling to produce generalised and quantified results(Bell, 2010). Therefore, it investigates the relationship between two events, by having specific and a clearly descriptive question. The advantage of using this method is it is easily comparable ,whereas the limitations can be the view of the participate sometimes isn’t fully reflected(Newman and Benz, 1998) . Qualitative research is collated to understand concept and perceptions of the participant in the study(Newman and Benz, 1998). By explaining ‘how’ and ‘why’ a certain phenomenon, or programme, happens as it does in a particular context. Qualitative research mostly investigates i) local knowledge and understanding of a given issue or programme; ii) people’s experiences, meanings and relationships and iii) social processes and contextual factors (e.g., social norms and cultural practices) (The Open University, 2018). By using this method it gives a clearer and broader understanding of the view and opinions of the participant , alongside producing reliable and unbiased results(Creswell and Plano Clarks, 2006). This will further be explored on how it was used within the questionnaire, in the development of the data collection tool section .
Sampling is when the researcher picks a handful of the population to investigate, enabling to give a wider understanding of the population(Thompson,2012). Quota sampling was the choice of sampling used, it can be defined as when participants are picked due to certain characteristics like age, sex, religion or profession in this case age(Henry, 1990). As this was a trial data collection peers, friends and family were recruited as participants, meaning the sample size was small; alongside enabling it to be both maintainable and manageable, upon collating all the information. It is argued by Babbie(2009) it is more efficient to have a smaller sample, “on the basis of knowledge of the population, it’s elements and the purpose of the study” in comparison to having significant numbers, just to have a large sample size.
Development of the data collection tool
The questions for the questionnaire were formulated through previous information with regard to ethnicity and achievement, enabling to find the limitations. This was done, due to information needed for the previous assignment, which supported the development of this research, analysing research is a highly suggested practice by Bryman(2004).
With in developing the questionnaire both close and open ended questions were used. Dixit(2007) defines close ended questions as when participants have various answers to choose from. The advantages of using these types of are: answers are more reliable, communicates the same reference to every individual, fast and easy to quantify. Open ended questions can be defined as answers which use the respondents own narrative explanation(Alreck and Settle,1995). The advantages of using these types of questions are; they useful in finding information about sensitive, controversial or taboo topics. Allowing the respondents to answer and describe in detail their genuine views, reiterate necessary content and the salience or priority of their informational concerns. Furthermore, enabling the participant to let off steam, ventilate their feelings and formulate explicit information that potentially would have not been produced, enabling to identify trends/patterns to further be explored and used(Brace,2013; Bell, 2005). Although the questionnaire was widely quantitative data through the use of closed questions, open questions allowed it to produce qualitative results, enabling it to meet the mixed methods approach criteria.
Within the questionnaire , the theme for the questions included; what GCSE grades they received(past),what they are doing currently and their experience within schools environment with teachers. Denscombe (2017) argues by setting themes for the questionnaire it able to make it more useful for future research. By doing this it is able to support that there was adequate planning in enabling a successful piece of research (Christian,2018).
Gaining ethical approval (including consent and tutor approval)
Ethical review from the Northampton University Research ethics committee was sought and gained . Various ethical factors were recognised from the onset for conducting the research, such as British Educational Research Association (BERA,2018) , the Framework for Research Ethics (ESRC, 2012) and the Data Protection Act 1998 (Legislation.gov.uk, 2018). Consent was required due to the complexity of the topic, which was going to be discussed. For instance, “ school experiences and academic achievement, which will all entail them to disclose their emotional and physical capabilities in that point in time of their life”. The participants will have a recall of both memories and experiences which could potential affect their holistic well being.
Prior to signing the consent form all the participants were given a participant information letter which followed the BERA(2018) and ESRC(2012) which clearly outlines : all participants must have knowledge of the way the research is going to be conducted, why they are involved within the research, how the data will be used and who will see the results of the research, appendix 2 is able to confirm this. The letter internalised all these aspects enabling it to be signed off by the Childhood and Youth Research module leaders, appendix 3 is able to confirm this. Furthermore, upon following both BERA(2018) and ESCRA(2012) guidelines, they state any research is required to have an informed consent form, whereby it must clearly state a way in which a participant can withdraw from the research. The research did meet this as all participant signed the consent form.
Carrying out the data collection
The study was carried out at Northampton College, prior to the study each participant was contacted enabling to arrange a suitable day enabling to meet their schedule, so they were able to do the questionnaire. Leavy(2017) would argue that this is able to show a good relationship between the researcher and participants have been built, potentially enabling more valid data.
Upon collecting the data, as stated before once the participants had signed and received their informed consent form and participant letter, when they were ready and confident to complete the questionnaire, the researcher left them with it, until they were ready to return the questionnaire. Rosenthal and Jacobson (1968) argued this is the best way to conduct research as it reduces the Hawthorne effect, this can be defined as when people adapt their behaviour accordingly, as they know they are being watched (Kirby,2000). Overall, this enables to increase the validity and representativeness of the research. Finally, the questionnaire was carried out over a 2 week period and it took each of the participants between 12- 15 minutes, it can be supported by Dörnyei and Taguchi(2009) that is was successful as the durations of the questionnaire didn’t exceed 30 minutes . The questionnaire was able to show clarity within the wording and layout as, when any participants collecting I wasn’t called back.
Brief feedback of findings
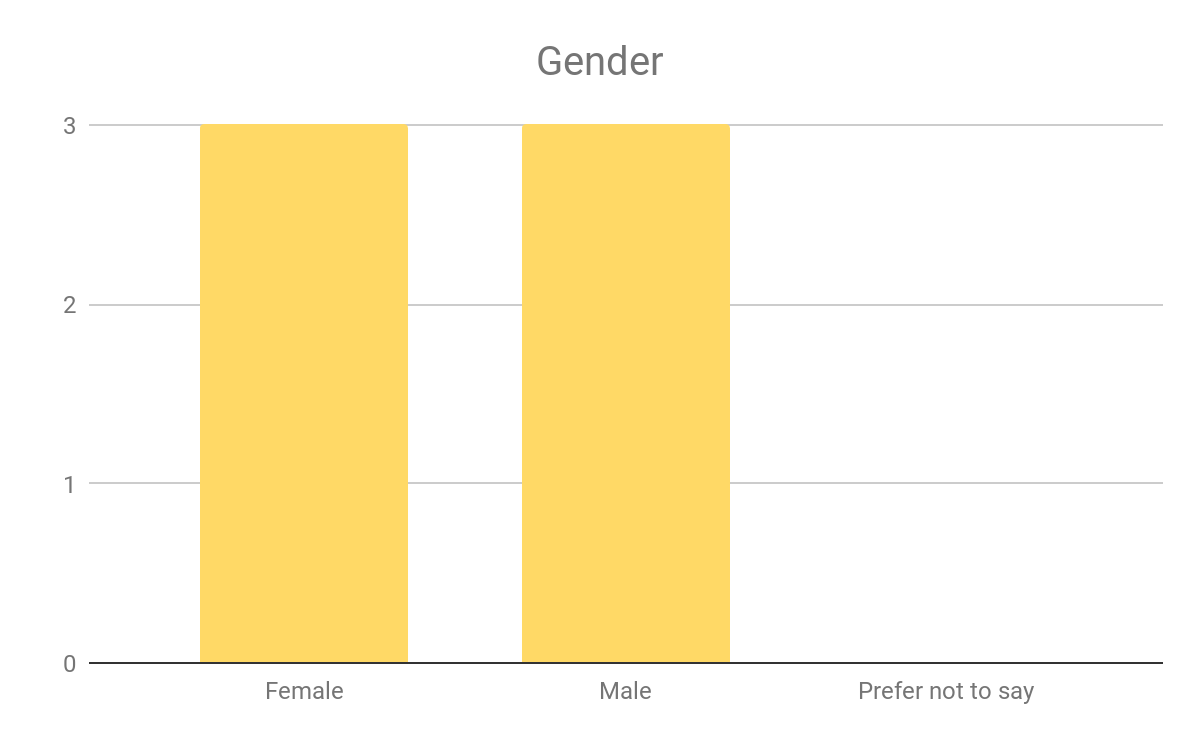
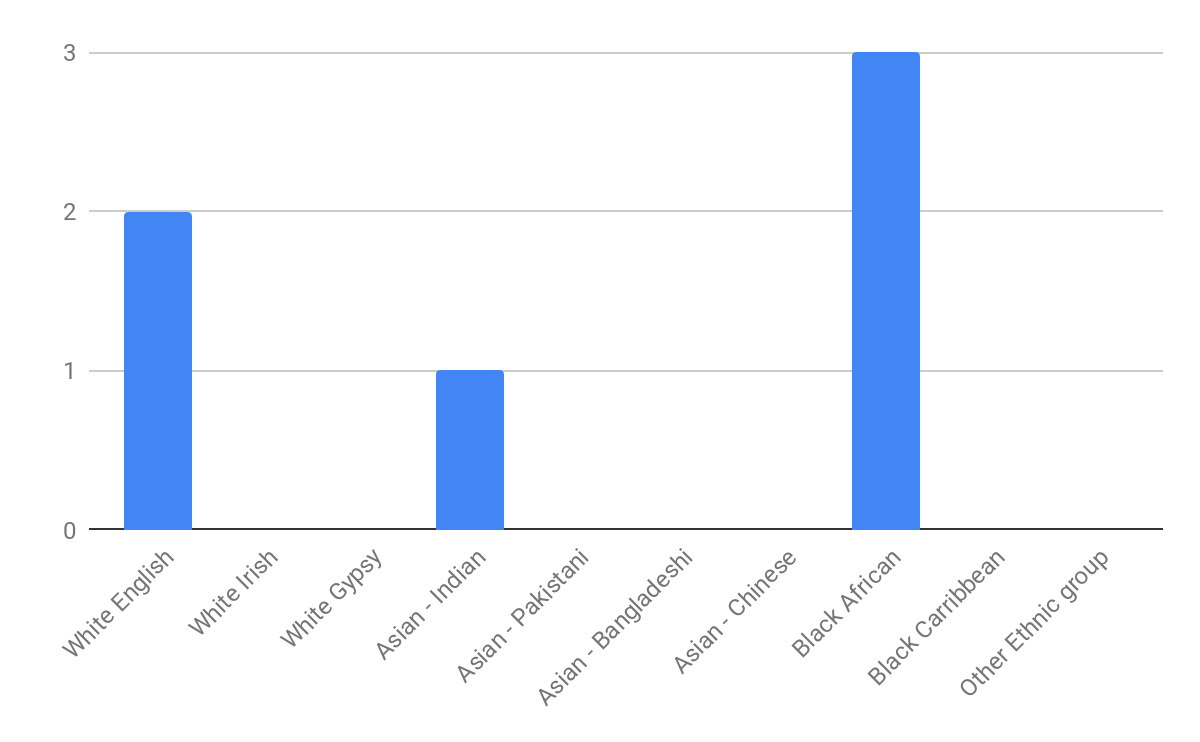
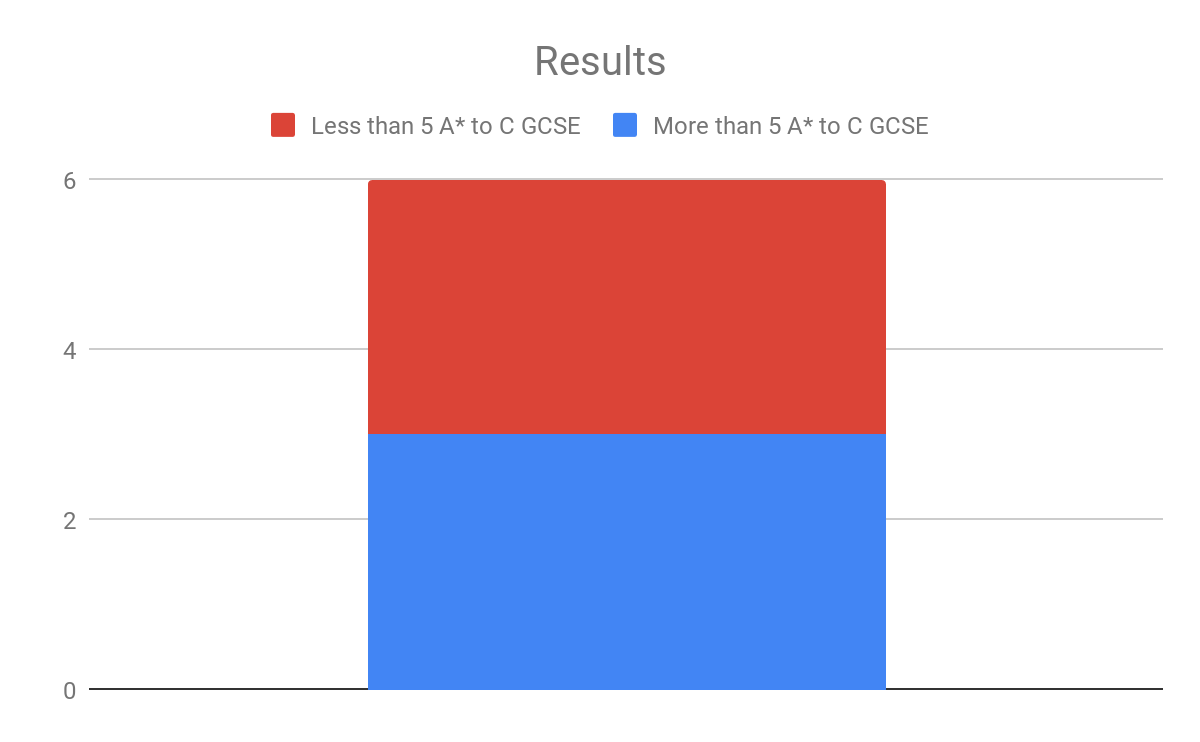
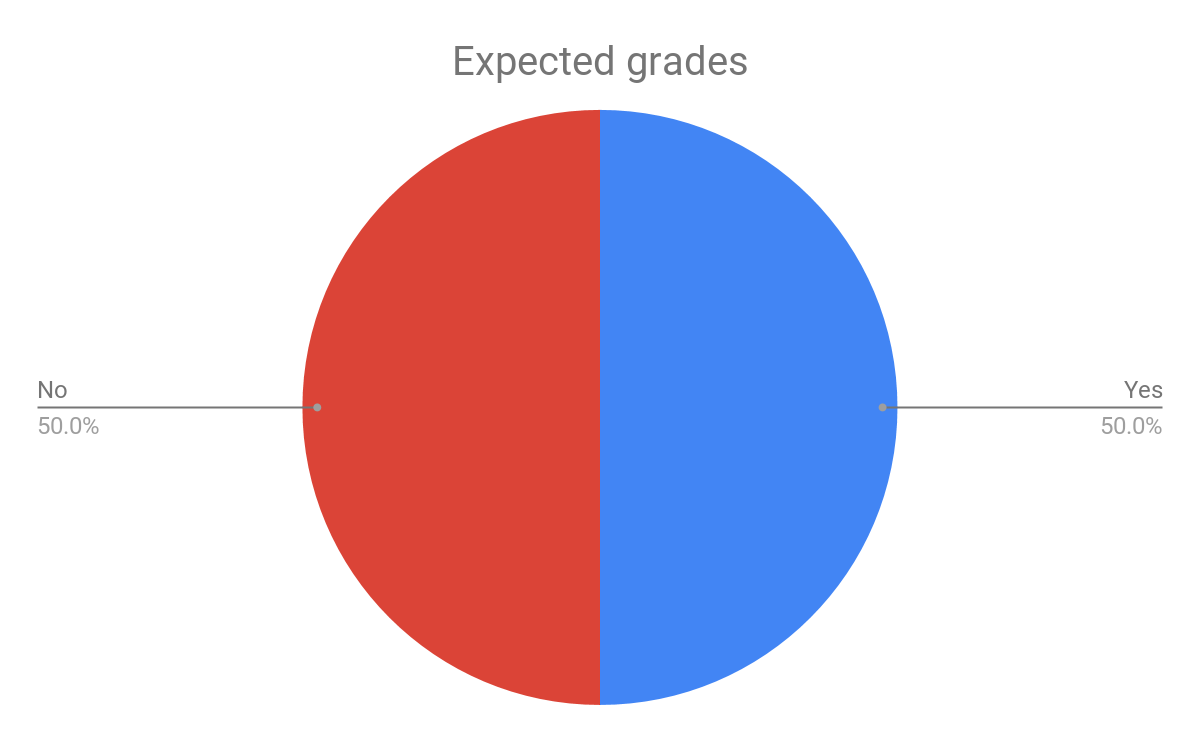
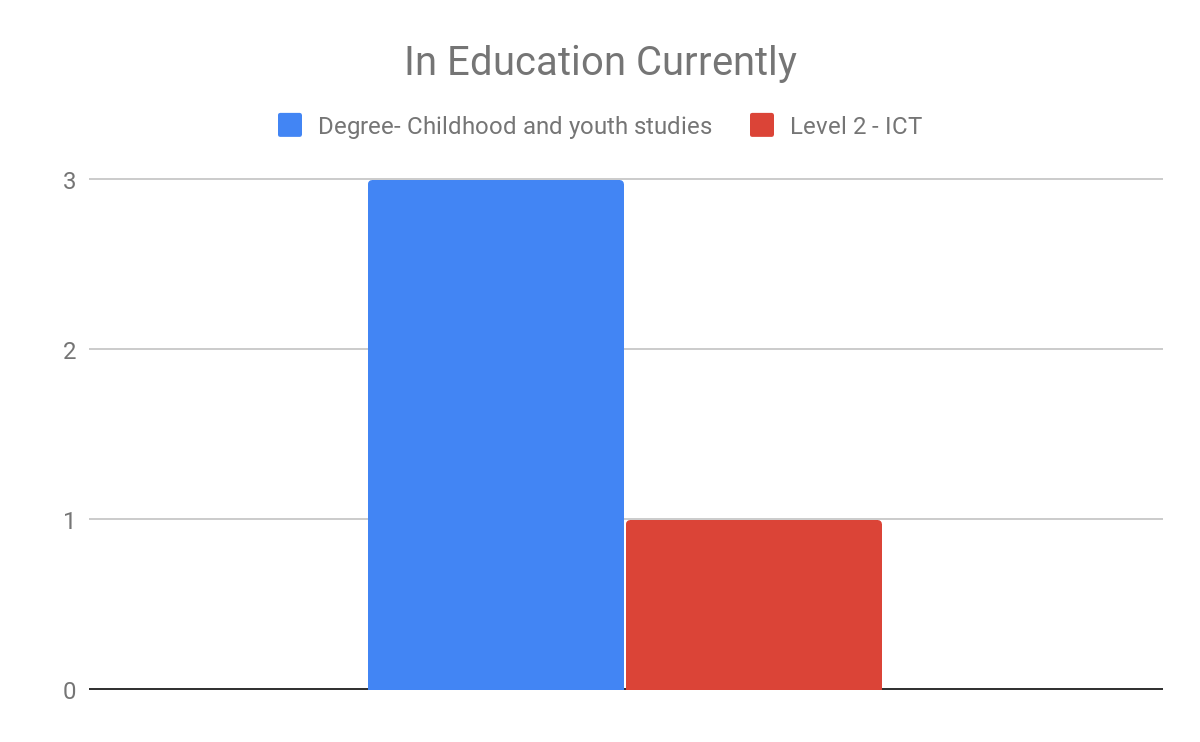
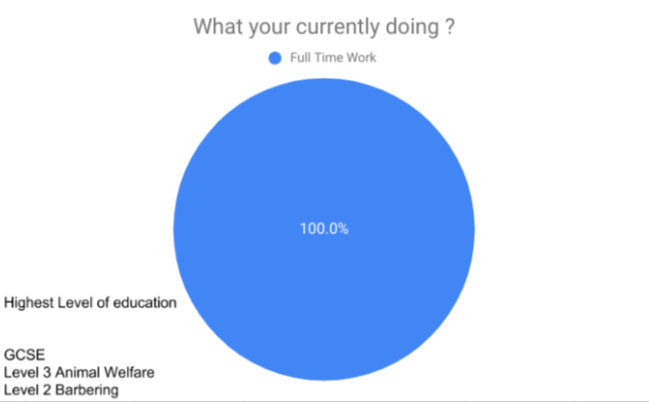
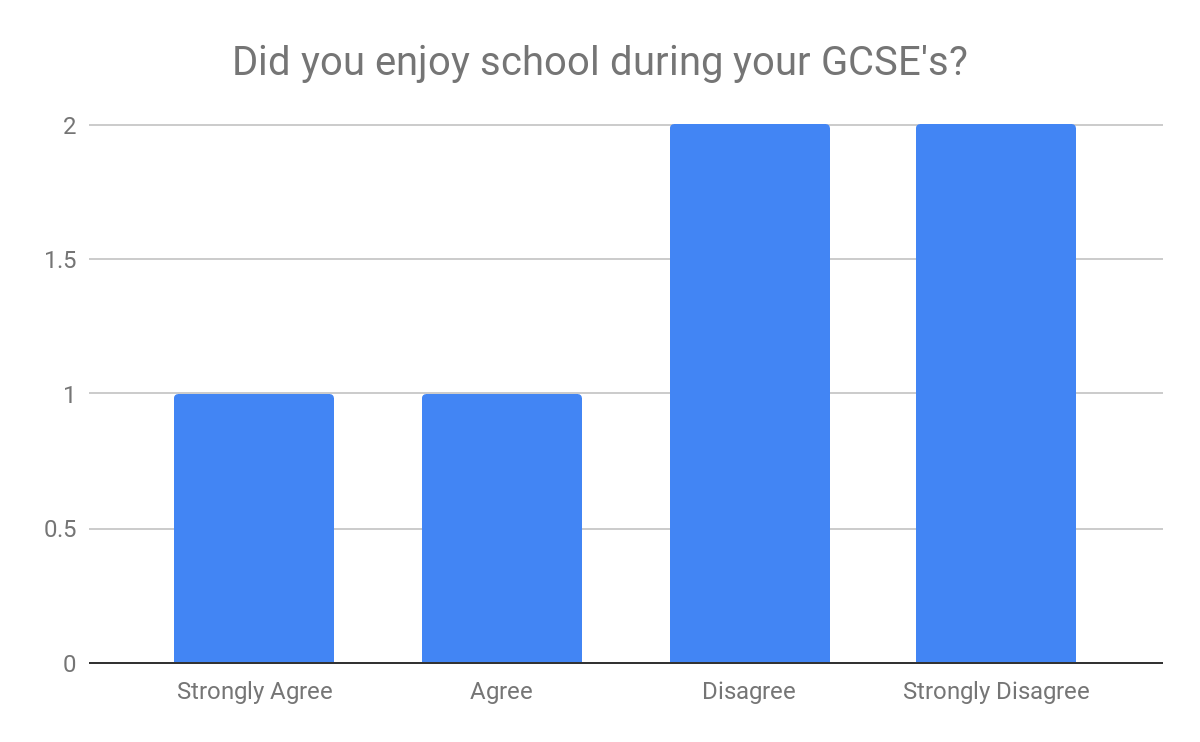
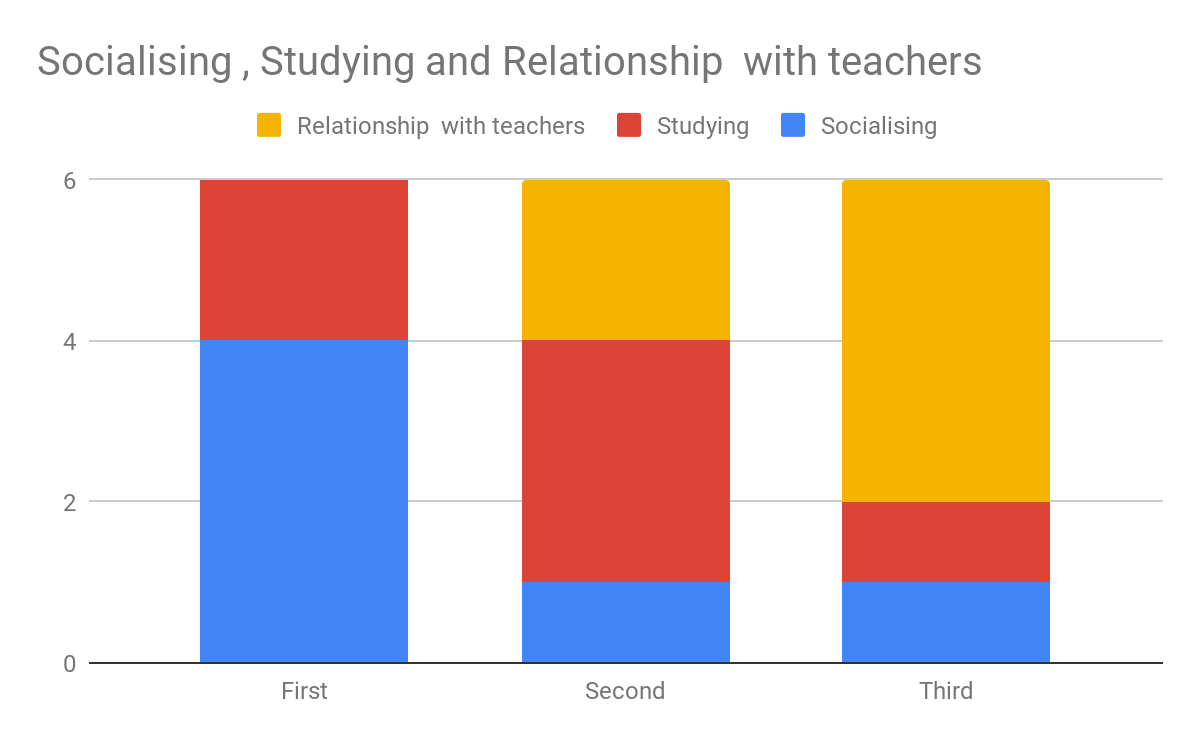
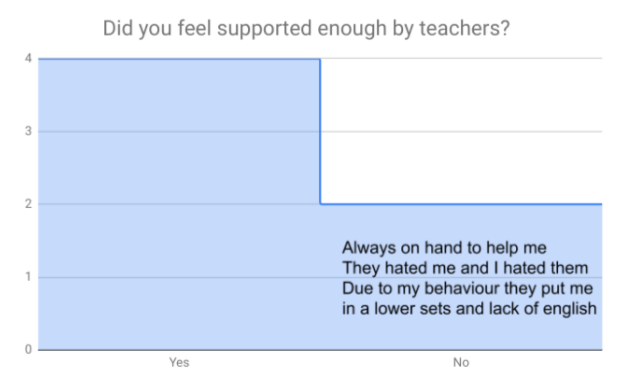
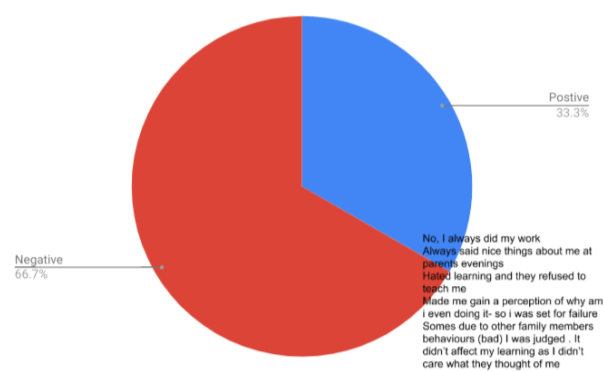
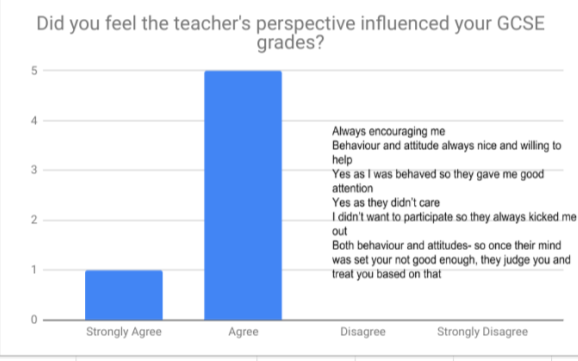
In analysing the questionnaires data, two consistent themes occured. The first theme was the representation that particular ethnic groups such as black african/ caribbean posed a fatalistic mindset. As previously mentioned in the research proposal this a concept argued by Stansfield(2016) that this mindset is a major factor that contributes to the underachievement of black boys within society. Another occuring theme that was also previously mentioned and researched was the difference between achievement between genders, girls overall were seen to achieve more leading them to currently be in higher education, this is a concept also argued by Alexander, R., Doddington, C., Gray, J., Hargreaves, L. and Kershner, R. (2012). Whereas the boys didn’t achieve nor meet the expected grades.
Overall, the questionnaire was able to find out more qualitative data, comparison to current literature or research that is currently available. However, it was able to support the literature and research that was also currently available. This enables to increase the validity and representativeness of their research.
Reflection on the process including your own learning and changes you
would consider for the future
Throughout the process of the reflection, I will be using Gibbs’ reflective cycle. In terms of the questionnaire it was successful by meeting the required percentage, enabling it to be representative enough. However, I personally thought as I was basing the sample size on individuals who wanted to participate , there would have been more of a response rate. This made me feel a little bit disheartened and curious. The bad experience was the fact that I felt that my study lacked aspects of representativeness and validity. The good experience and it made me sense, upon doing my research it made me realise that next time I could use a different sampling method. To eliminate this next time, I would change the time period in which the questionnaire was conducted, Druckman (2005), argues that festive period such as christmas hinder outcome as individuals are both personally and academically busy. Another factor, that should have been included within my questionnaire was in regards to family structure, as within my literature research it was able to identify that it has an impact on the academic achievement of a young person.
Find Out How UKEssays.com Can Help You!
Our academic experts are ready and waiting to assist with any writing project you may have. From simple essay plans, through to full dissertations, you can guarantee we have a service perfectly matched to your needs.
View our academic writing services
Overall, preparing and carrying out the questionnaire had challenging aspects within in, it was able to identify that it doesn’t go all as planned intentionally. This made me realise the importance of resilience and adjustability, when doing research. Finally, on reflection I should have taken my role more professionally, as the way they viewed me had affect on my study. Upon doing some of the questionnaires with some of the younger males they found the idea of the research funny. Kobayashi(1994) was able to identify that gender has a huge influence on research. Therefore women are more likely to be discriminated. I am not saying that this was highly visible but you could see underlying behaviours of this. I have felt that this conducting this pilot research has been a good learning curve enabling to give me an insight of what is expected within my graduation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the pilton research questionnaire was successful meeting all the ethical and practical guidelines , alongside supporting current research in regard to ethnicity and achievement. It was able to outline that there is still a major difference of GCSE achievement according to both gender and ethnicity. This is due to several factors such as internal(school) or external (personal) factors have greater influence on academic achievement, which were explained in the research proposal. These all need reconsidered to enable the child to reach their full potential regardless of their background .
Bibliography
- Alexander, R., Doddington, C., Gray, J., Hargreaves, L. and Kershner, R. (2012). The Cambridge Primary Review Research Surveys. Hoboken: Taylor and Francis.
- Alreck, Pamela L & Settle, Robert B 1995, The survey research handbook, 2nd ed, Irwin Professional Publishing, Burr Ridge, Illinois
- Babbie, E. (2009). The Practice of Social Research. (12th ed.). Belmont: Wadsworth Publishing.
- Bell, J. (2005). Doing your Research Project. (4th ed.). Maidenhead: Open University Press.
- BELL, J. (2010). Doing your research project: a guide for first-time researchers in education, health and social science. Maidenhead, McGraw-Hill Open University Press. http://public.eblib.com/choice/publicfullrecord.aspx?p=771407.
- Book Review: Creswell, J. W., & Plano Clark, V. L. (2006). Designing and Conducting Mixed Methods Research. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage
- Brace, I. (2013). Questionnaire Design: How to Plan, Structure and Write Survey Material for Effective Market Research. London: Kogan Page Publishers.
-
British Educational Research Association (BERA). (2018). Ethical guidelines for educational research.
London, BERA. - Bryman, A. (2004). Social Research Methods. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Bryman, A. (2008) Social Research Methods. 3rd edn. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Christian, K. (2018). Keys to Running Successful Research Projects: All the Things They Never Teach You. United States: Academic Press.
- Denscombe, M. (2017). The Good Research Guide- For Small-scale Social Research Projects. London: Open University Press.
- Dixit, J. (2007). Structured System Analysis and Design. 1st ed. Firewall Media.
- Druckman, D. (2005). Doing research. Thousand Oaks, Calif.: Sage publications.
- Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC) (2012). Framework for Research Ethics. Retrieved on 11th February 2013, from: http://www.esrc.ac.uk/_images/Framework-for-Research-Ethics_tcm8-4586.pdf
- Gillham, B. (2008). Developing a questionnaire (2nd ed., Real world research). London: Continuum.
- Henry, G. (1990). Practical sampling. Applied social research methods, 21.
- Kirby, M. (2000). Sociology in perspective for OCR. Oxford: Heinemann.
- Kobayashi, A. (1994). coloring the Field: Gender, “Race,” and the Politics of Fieldwork. The Professional Geographer, [online] 46(1), pp.73-80. Available at: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/citedby/10.1111/j.0033-0124.1994.00073.x?scroll=top&needAccess=true [Accessed 17 Dec. 2018].
- Leavy, P. (2017). Research design Quantitative, Qualitative, Mixed Methods, Arts-Based, and Community-Based Participatory Research Approaches. United States: Guilford Publications.
- Legislation.gov.uk. (2018). Data Protection Act 1998. [online] Available at: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/1998/29/contents [Accessed 21 Dec. 2018].
- Newman, I. and Benz, C. (1998). Qualitative-quantitative research methodology. Carbondale: Southern Illinois University Press.
- Stanfield II, J. (2016). Black Reflective Sociology. New York: Routledge.
- Taguchi, T. and Dörnyei, Z. (2009). Questionnaires in Second Language Research: Construction, Administration, and Processing. London: Routledge.
- The Open University. (2018). 6 Methods of data collection and analysis. [online] Available at: http://file:///home/chronos/u-93a2a6441199742e41a55d06f65118c76e672ea2/Downloads/6%20methods%20of%20data%20collection.pdf [Accessed 18 Oct. 2018].
- Thompson, S. (2012). Sampling. John Wiley & Sons, (US).
Appendix list
Appendix 1 
Appendix 2
Appendix 3
Appendix 4
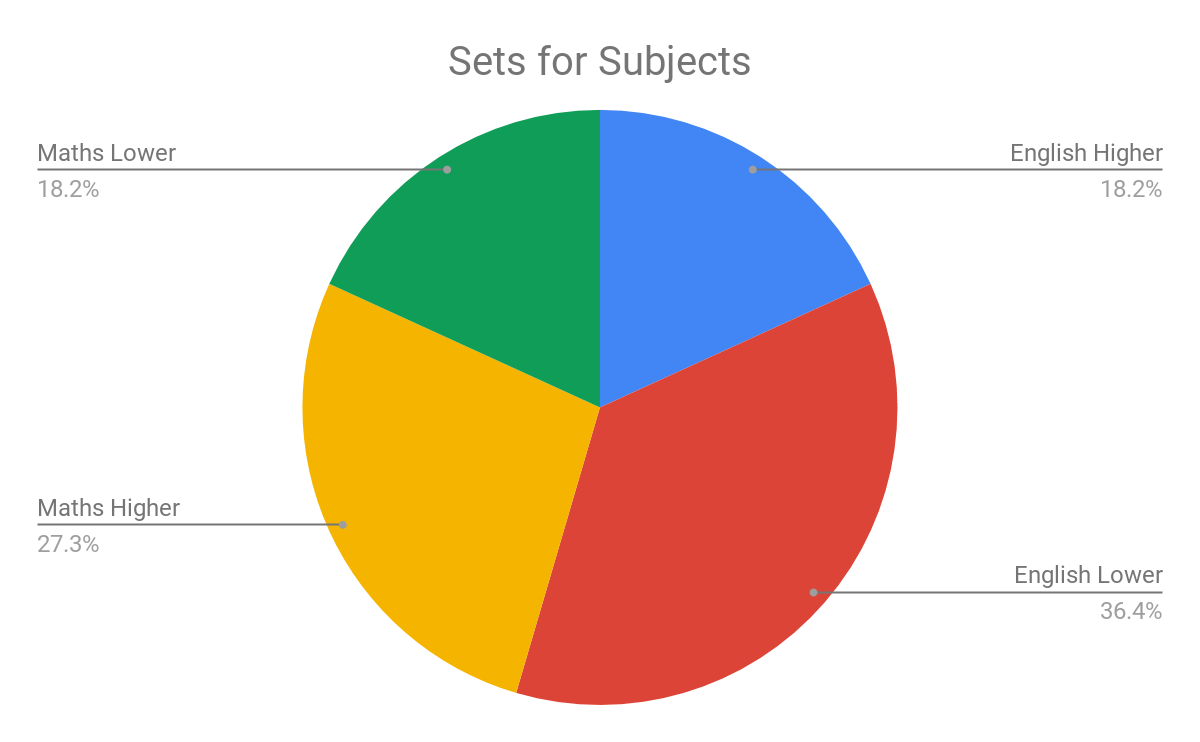
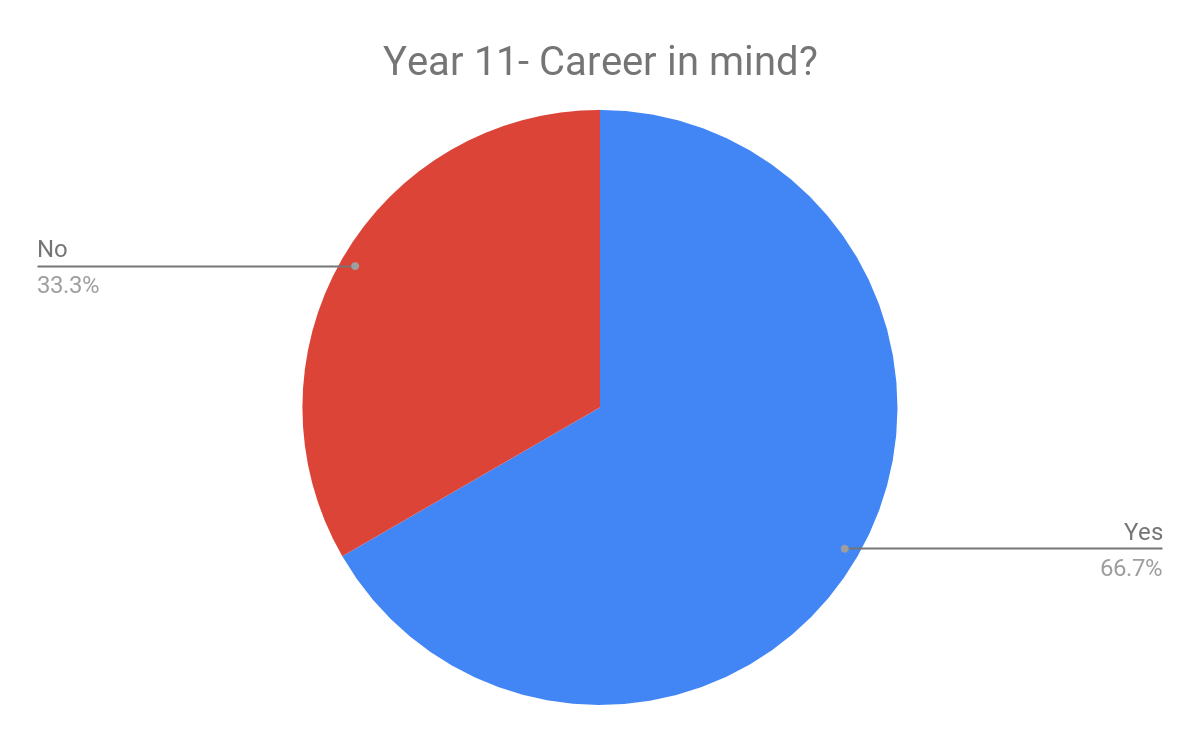
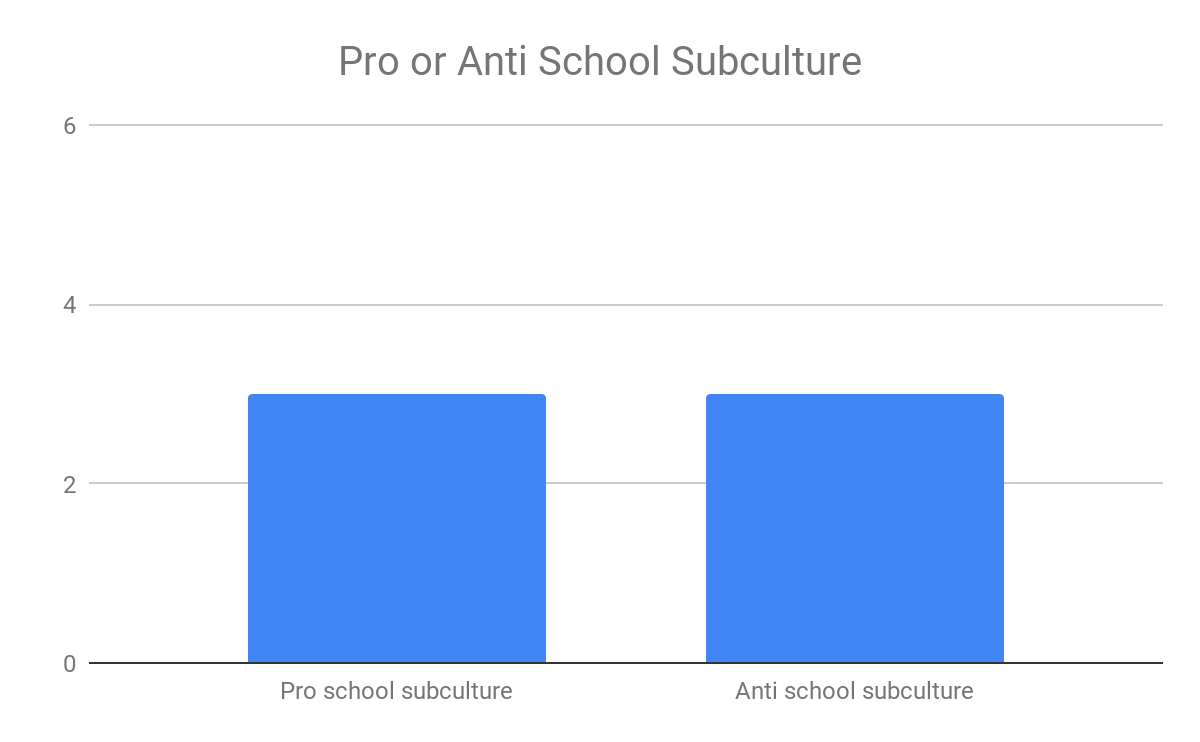
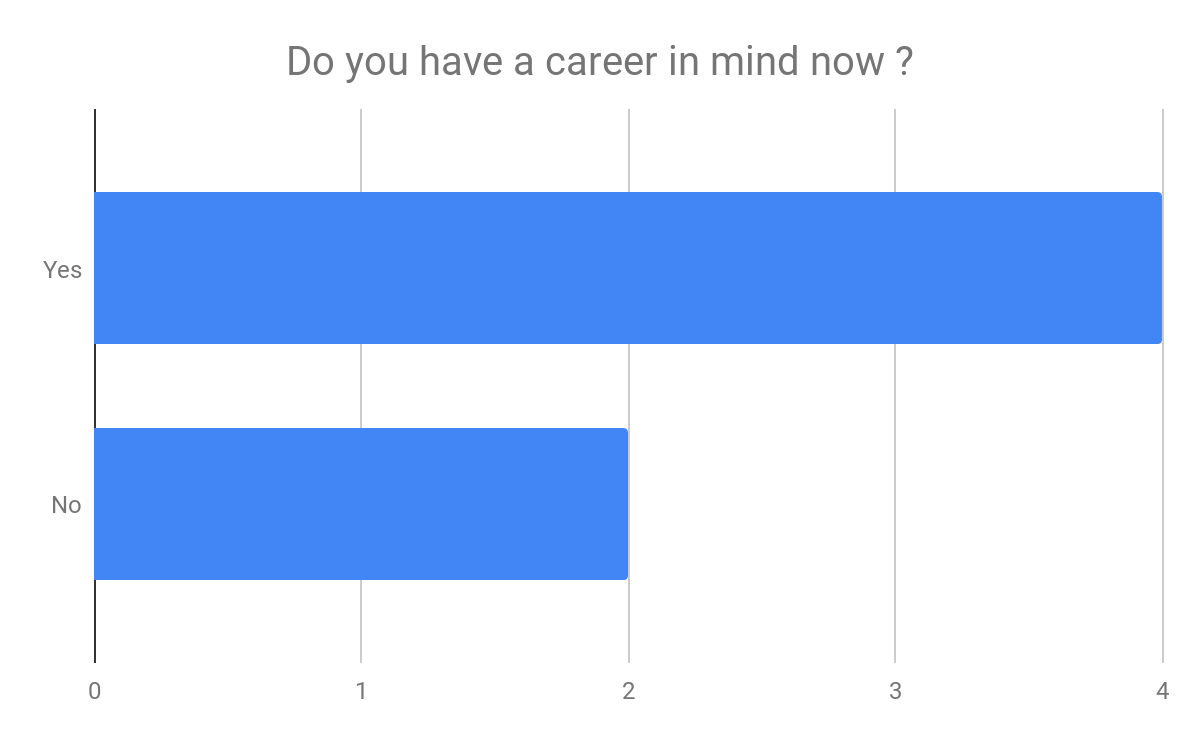
Social work
Youth Offender
Millionaire
Primary School teacher
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:


