Automobile engines have been definitely improved in the course of recent years that they have been delivered. Engines have made life a lot simpler. They give a progressively proficient strategy for voyaging. Individuals don't have a clue how much the world has changed, because of the activity of the motor. The engine is an extremely unpredictable bit of hardware.
The historical backdrop of combustion engines goes back in the year 1680 when Christian Huygens, a Dutch physicist tried different things with them (Daniels, 2003). Below diagram represents different parts of the engine.
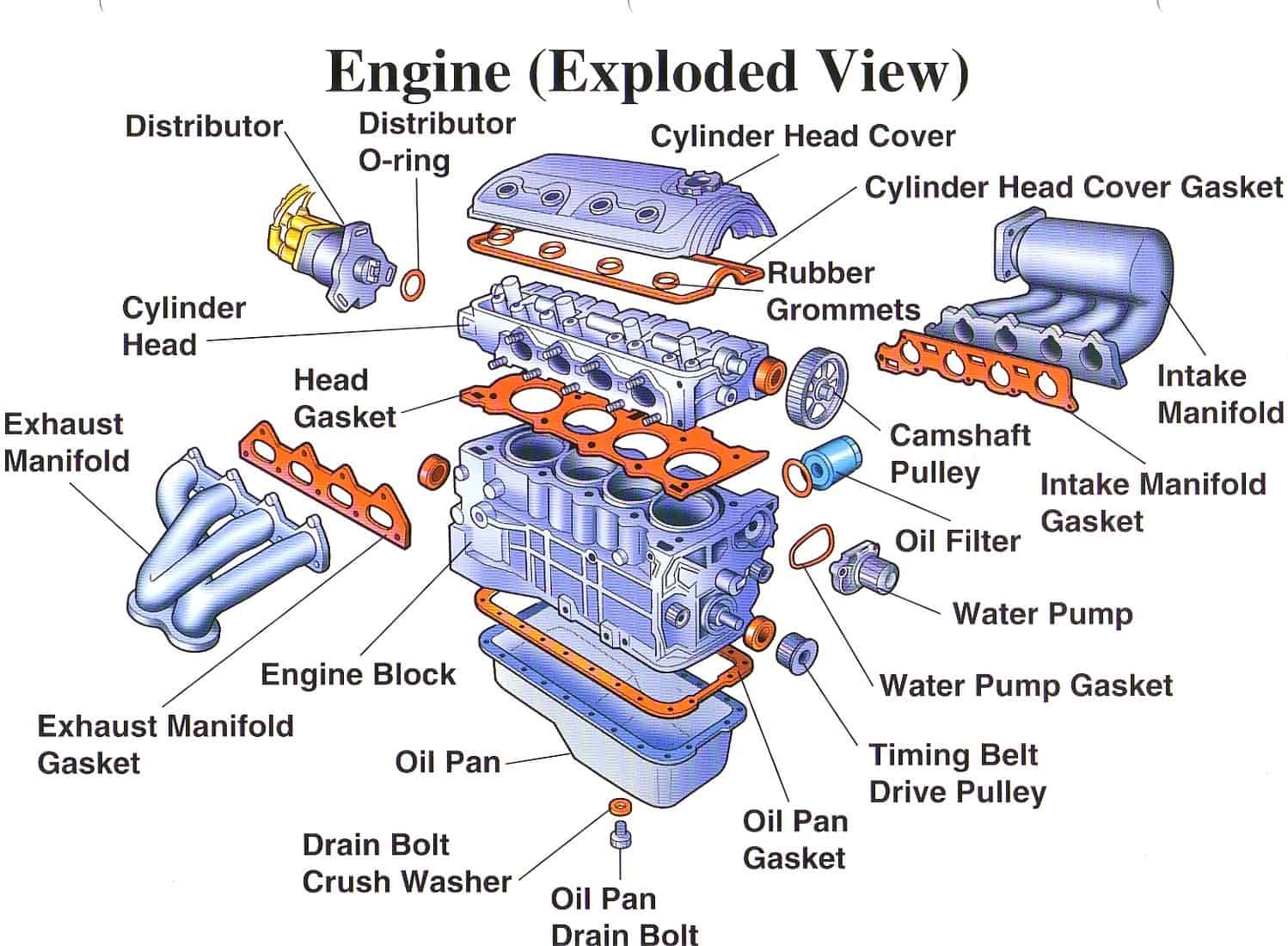
FIG 1: Engine (1)
Gottlieb Daimler in 1885 manufactured a littler and quick paced adaptation of the advanced gas motor that had a vertical chamber and devoured fuel constrained by means of the carburetor.
Following four years, a similar American specialist developed a four-stroke motor expecting a mushroom-molded valves and twofold chambers situated in a V-shape with a higher proportion of capacity to that of weight. This motor didn't have the electric start until 1924 when creations of one demonstrated conceivable. In any case, fuel engines being used today can follow their roots from Daimler's engines.
Working of Engine
For understanding the working of the engines first we have to understand the types of engines. Basically the engines are of two types, and these are external combustion engines and internal combustion engines.
(i). External combustion engine: In external combustion engine, the burning of fuel happens outside the motor. Ex.: Steam Engine.

FIG 2: Steam Engine (2)
(ii). Internal combustion engine: In internal combustion engine, the ignition of fuel happens inside the engine. Two stroke and four stroke oil and diesel engines are the instances of inside burning motor.
Working of an engine:
- Ignition Stroke: Air and fuel mixture in case of spark ignition and just air in case of compression ignition, is sucked from the inlet valve by the downward movement of the piston.
- Compression Stroke: Mixture of fuel and air inside the cylinder is compressed at certain compression ratio and above its ignition temperature.
- Power Stroke: Spark is ignited from the spark plug (spark-ignition) and fuel is injected in case of diesel engine. Due to high pressure explosion takes place and piston is pushed down which gives the power stroke.
- Exhaust: Piston moves upward and ejects the burnt fuel out of cylinder from the exhaust valve.
Methods of reducing the fuel consumption in engines
In the course of the most recent 30 years, innovative work has helped makers decrease ICE discharges, for example, nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate issue (PM) by over 99% to consent to EPA emissions standards. Research has likewise prompted enhancements in ICE execution and productivity, helping manufactures maintain or decrease the fuel consumption.
Below are some methods to decrease the fuel utilization in engines:
Turbocharging:
A turbocharger is essentially a pneumatic machine, driving additional oxygen into the motor varying so it can consume more fuel to make more power. In a turbocharged motor, the turbo siphons in a higher volume of air under pressure, and the vehicle Electric control unit (ECU) reacts by including the right measure of extra fuel.
The turbo is controlled by the exhaust gases. One side of the turbo is situated at the ventilation system, the other at the engine's air intake, and it contains two little fans joined by a shaft. As fumes goes through the turbo, it turns one fan, called the turbine. This thus turns the subsequent fan, called the blower, which draws outside air, pressurizes it, and powers it into the motor. The difference between atmospheric pressure and the measure of air pressure the turbo gives is known as boost, and is estimated in pounds per square inch (psi). Below figure shows the cut-section view of the Turbocharger.
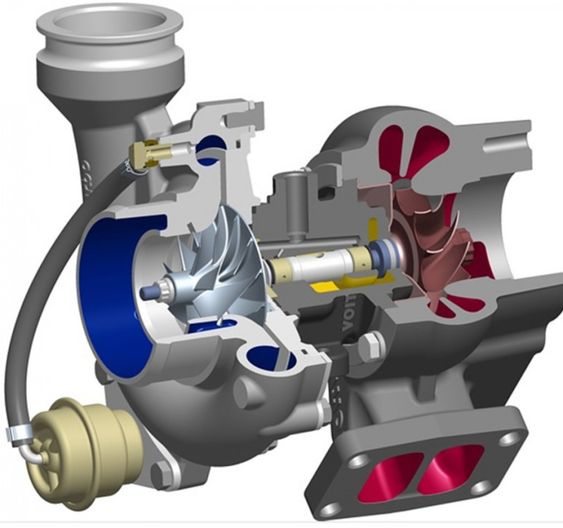
FIG 3: Turbocharger flow diagram (3)
Dual Ignition (Twin spark Plug Technology):
Double Ignition is a framework for sparkle start motors, whereby basic start parts, for example, flash fittings and magnetos, are copied. Double start is most generally utilized on air engines, and is in some cases found on vehicles and cruisers.
Double start gives two focal points: excess in case of in-flight disappointment of one start framework; and increasingly effective consuming of the fuel-air blend inside the burning chamber. In Airplane, repetition is the prime thought, however in different vehicles the principle targets are proficient ignition and meeting discharge law necessities.
The graph compares the ignition timing for the Dual Sparked 67 Horsepower Air Head engine.

FIG 4: Dual spark timing curve (4)
EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation):
In inside ignition motors, exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) is a nitrogen oxide (NOx) emanations decrease strategy utilized in oil/fuel and diesel motors. EGR works by recycling a segment of a motor's fumes gas back to the motor chambers. This weakens the O2 in the approaching air stream and gives gases idle to burning to go about as sponges of ignition warmth to diminish top in-chamber temperatures. NOx is delivered in high temperature blends of air nitrogen and oxygen that happen in the burning chamber, and this generally happens at chamber top weight. Another essential advantage of outer EGR valves on a sparkle start motor is an expansion in productivity, as charge weakening permits a bigger throttle position and diminishes related siphoning misfortunes.
The picture shows the schematic representation of a high-speed passenger car EGR/intake throttle system for Euro 3 application of Audi 3.3 L V8 TDI engine
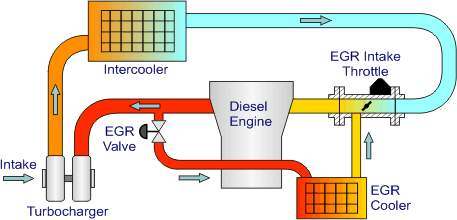
FIG 5: EGR (5)
Diesel vs Hydrogen Engine
A hydrogen internal combustion engine vehicle (HICEV) is a kind of hydrogen vehicle utilizing an interior ignition motor.
Below are the key points and advantages of the Hydrogen engine over the diesel engine which helped in the reduction and conservation of the fuel:
- hydrogen in double fuel activity indicated a decline of the base brake explicit fiery utilization by around 8 % contrasted with standard diesel motor.
- at the hydrogen-diesel oil double fuelling activity mode NOx outflows level reductions with 12% near to diesel motor for a 2.62% percent of substitute proportion of diesel fuel by hydrogen.
- the HC and smoke outflows level gradually diminishes at the hydrogen expansion increment contrasted with standard diesel motor
- hydrogen likewise at diesel fuel is a promising elective fuel for pressure start motors.
- the utilization of the hydrogen likewise at diesel fuel by diesel-gas fuelling technique doesn't required significant motor structure modifications.
Conclusion
From the above factors we came to conclude that the Turbochargers enhances the efficiency to the great level and helps in the fuel consumption however the best efficiency and consumption was found in Hydrogen Engines. Even the byproduct of the Hydrogen engine is water which is not harmful for the Environment too. Additionally, hydrogen is abundant and is a renewable source of fuel which so beside a better efficient fuel it works in saving the environment too from the harmful gases like Nitrous oxide and Sulphur dioxide. Whereas petrol and diesel engine release harmful gases like carbon monoxide and NOx etc. Many automobile companies are working on their future concept vehicles and airplanes on this which would be helpful for both us and the environment.
References
- pininterest.ca
- energy.gov
- driving.ca/auto-news/news/how-it-works-turbocharging
- G. Karim, Hydrogen as a spark ignition engine fuel, International Journal Hydrogen Energy, 2003, 56:256e63.
- Exhaust Emissions and Driveability – Chrysler Corporation, 1973
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:


